


| Home | Parent | ← Go → | Prior | Next |




A Collection(), and all supported browser apps, can contain several types of items: bookmarks, folders, and separators. We refer to these item types collectively as bookmarks content items, or just content …
A bookmark is a reference to a URL on the internet. Besides the URL, a bookmark can have several other attributes such as its name, tags, comments (description), shortcut key, lineage, and various statistics. What we call a bookmark is called url in Pinboard.
Although they can look similar other folders, most web browsers have two or three of what we call hard folders. Like the hardware inside your computer, you cannot change the name or location of a hard folder by typing with your keyboard or clicking with your mouse.
To replicate what you see in your web browser, a Collection has hard folders. You can recognize the hardness because their names are displayed in italics, as shown here:

A Collection may have zero, one, two, three or four hard folders. Hard folders are present or absent in a document, depending on its structure.
In order to map content items during Import and Export operations, Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster needs to identify equivalences between its own hard folders and those of web browser apps. The table below shows the mappings.
The Hard Folders displayed in the app are named to match the name of the Hard Folder in the first of the document’s Browsers (Clients) which has such a folder. In case that no browser (client) has a Hard Folder corresponding to a given Hard Folder existing in the app, the app defaults to these names: Favorites Bar, Other Bookmarks, Reading List, and My Shared Bookmarks.
| Possible Name as displayed in Smarky, Synkmark, or BookMacster | Favorites Bar or Bookmarks Bar |
Other Bookmarks | Reading List or Unsorted Bookmarks |
My Shared Bookmarks |
| The original idea behind this hard folder | Appears in the toolbar (near the top) of windows | “Overflow” which cannot fit in the toolbar | A special place to quickly drop new bookmarks which you will put in a better place, later. | A special place for bookmarks that will be shared with other people. |
| Brave, Chrome, Canary, [FreeSMUG’s Chromium](http://www.freesmug.org/chromium), Epic | Bookmarks Bar | Other Bookmarks | - | - |
| Edge | Favorites Bar | Other Favorites | - | - |
| Firefox | Bookmarks Toolbar | Other Bookmarks | Unsorted Bookmarks | - |
| iCab | - | - | - | - |
| OmniWeb | Favorites | Personal Bookmarks | - | My Shared Bookmarks |
| Opera | Bookmarks Bar | My Folders | Unsorted Bookmarks | Speed Dial |
| Orion | Favorites | Bookmarks Bar | - | - |
| Safari | Favorites Bar | - | Reading List | - |
| Vivaldi | - | - | - | - |
| Delicious, Diigo, Pinboard | - | - | - | - |
In contrast to the Hard Folders, we speak of Soft Folders as the regular folders you create in Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster or in a web browser app. For example, folders named News or Vacation Ideas are soft folders that you’ve created. In contrast the hard folders, you may rename, move or delete soft folders as you wish.
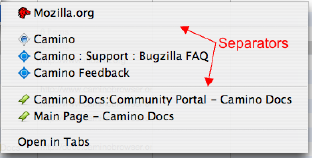
Separators, also called separator lines, are little “fences” that may be placed between groups of items that are still in the same parent folder.
Attributes are the charactertistic of bookmarks and other content items. For example, some of the attributes of Bookmarks Content items are: name, url, shortcut, tags, comments, date added, visit count.
Although most attributes are self-explanatory, in this section we explain those that are not…
There are three URLs which Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster store for a bookmark:
Current URL is the URL that would currently be used if you clicked Visit, and the URL that would be passed to a Client during an Export.
Suggested URL is likely a better, newer one which Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster has received, usually as the result of a redirection from the website, during a Verify operation.
Prior URL is just a holding place for a URL that was replaced, in case you want to revert to it later.
You can see all three URL of a selected bookmark by opening the Inspector panel and opening its bottom sidebar.
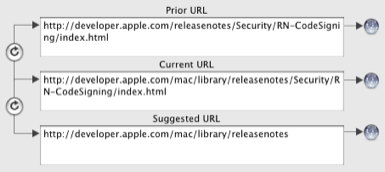
Clicking one of the buttons on the left will swap the indicated URL values.
Clicking one of the buttons on the right will visit the site addressed by the adjacent URL.
In the Inspector Panel, next to the name of the subject item is a rectangle called a color well. After clicking this color well, you can set the text color which used is to display the item’s name in the Content View, Menu Extra, and contextual menus. This attribute is not supported by any clients and is therefore not exported. It is for your use within Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster only.
This attribute sets explicitly whether or not a particular folder will be sorted when sorting is done. In addition to the checkbox in the Inspector, this is also indicated by the folder’s background color and symbol in the Content Tab.
The response from a website to a request for a bookmark’s URL normally contains an HTTP Status Code, which is usually a positive integer between 100 and 599, although some creative cowboy webmasters sometimes return their own made-up status codes, usually in the range 600 to 999.
However, “lower level” errors can occur if the site does not send an HTTP response. These lower level errors are returned to Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster by macOS and contain “error codes” in Apple’s NSURLErrorDomain. The codes in NSURLErrorDomain are negative numbers.
Fortunately (maybe because Apple planned it this way), there is no overlap between these positive and negative values. Therefore, Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster stores in its Verify results for a bookmark what we call a Verify Status Code. Quite simply, if this value is positive, it’s an HTTP Status Code, and if negative, it’s an error code in the NSURLErrorDomain.
Most of the HTTP status codes you will see are defined in Section 10 of Internet Society’s specification HTTP/1.1. But although it was published in 1999, this document still has not been ratified into a standard, and in the meantime additional codes have been proposed. For a readable and more complete table of the HTTP status codes in use at this time, we recommend this Wikipedia article.
The following is derived from the file NSURLErrorDomain.h, but we’ve published them here since you will not have that file unless you have installed Apple’s Developer Tools, and also we added the narrative descriptions.
| Code | NSURLError: | Means that connection failed because: |
| -999 | Cancelled | it was cancelled. |
| -1000 | BadURL | it has a bad URL. |
| -1001 | TimedOut | it took longer than the timeout which was alotted. |
| -1002 | UnsupportedURL | it has an unsupported URL. |
| -1003 | CannotFindHost | the host could not be found. |
| -1004 | CannotConnectToHost | the host would not let us establish a connection. |
| -1005 | NetworkConnectionLost | we established a connection but it was lost. |
| -1006 | DNSLookupFailed | domain name server (DNS) lookup failed. |
| -1007 | HTTPTooManyRedirects | we received too many redirects from the server while processing the request. |
| -1008 | ResourceUnavailable | the requested resource is not available. |
| -1009 | NotConnectedToInternet | this computer appears to not have an internet connection. |
| -1010 | RedirectToNonExistentLocation | we were redirected to a nonexistent location. |
| -1011 | BadServerResponse | we got a bad response from the server. |
| -1012 | UserCancelledAuthentication | the user cancelled when asked for authentication. |
| -1013 | UserAuthenticationRequired | user authentication is required. |
| -1014 | ZeroByteResource | the requested resource contains no data. |
| -1015 | CannotDecodeRawData | we could not decode the raw data. |
| -1016 | CannotDecodeContentData | we could not decode the content. |
| -1017 | CannotParseResponse | we could not parse the response. |
| -1100 | FileDoesNotExist | the requested file does not exist. |
| -1101 | FileIsDirectory | the requested file is in fact a directory. |
| -1102 | NoPermissionsToReadFile | we lack sufficient permissions to read the requested file. |
| -1103 | DataLengthExceedsMaximum | the length of the requested data exceeds the limit. |
| -1200 | SecureConnectionFailed | we could not establish a secure connection. |
| -1201 | ServerCertificateHasBadDate | the server’s SSL certificate appears to have expired. |
| -1202 | ServerCertificateUntrusted | the server’s SSL certificate is not trusted. |
| -1203 | ServerCertificateHasUnknownRoot | the server’s SSL certificate has an unknown root. |
| -1204 | ServerCertificateNotYetValid | the server’s SSL certificate is not yet valid. |
| -1205 | ClientCertificateRejected | the server rejected our client certificate. |
| -2000 | CannotLoadFromNetwork | we could not load from the network. |
| -3000 | CannotCreateFile | we could not create a file. |
| -3001 | CannotOpenFile | we could not open a file. |
| -3002 | CannotCloseFile | we could not close a file. |
| -3003 | CannotWriteToFile | we could not write to a file. |
| -3004 | CannotRemoveFile | we could not remove a file. |
| -3005 | CannotMoveFile | we could not move a file. |
| -3006 | DownloadDecodingFailedMidStream | decoding the downloaded data failed in midstream. |
| -3007 | DownloadDecodingFailedToComplete | decoding the downloaded data failed to complete. |
HTTP Status Code 302 should be returned by a website when there has been a temporary redirect that should not be used permanently. For example, you may have a bookmark to the Hooterville News newspaper with the url
http://www.hootervillenews.com/todaysHeadlines
This URL takes you to today’s headlines. However, you won’t get there directly. In response, today, their server will send back a response with HTTP Status Code 302, including a redirect to the url:
http://www.hootervillenews.com/headlines/2009_07_16
which will give you the headlines for today, July 16. Your browser then visits this redirect URL and renders its data instead of the URL you asked for.
Now. if you click on that same bookmark tomorrow, you will again get a 302 response but will be redirected to a different url:
http://www.hootervillenews.com/headlines/2009_07_17
which will give you the headlines for tomorrow, July 17.
This example illustrates the correct usage of the 302 status code by the Hooterville News.
Note that, in this case, you would not want to update your bookmark to point to the redirected url, because if you did, you would be reading July 16’s headlines forever.
Last Modified is an attribute supported by Firefox, Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster. It is imported or exported to Firefox during an Import or Export operation.
Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster update the Last Modified of an item whenever any of its nontrivial attributes are changed. In addition, the app updates the Last Modified of a folder whenever it gains or loses a child item. Therefore, when you move an item from one folder to another, although the Last Modified date of the item itself (or any of its descendants, if it is a folder) is not changed, the Last Modified date of the old and new parent folders are set to the current date and time.
As practiced by Firefox, Last Modifed is the last time that any of the bookmark’s attributes such as Name or Comments (Description) were modified. Moving the bookmark does not count as a change in attributes, and neither does changing tags (probably because Firefox considers ‘parent’ and ‘tags’ to be ‘relationships’ and not ‘attributes’). Note that the Last Modified attribute has to do with the bookmark itself and not with the bookmarked website. That is, Last Modified does not change when the site’s webmaster changes the content of the site.
Finally, note that, as of Firefox 3.5, the Last Modified attribute, although updated as noted above, is not visible in Firefox itself.
Bookmarks and folders have an attribute which allows you to exclude the from being exported to selected Clients. To access these switches, activate the Inspector and click the Export Exclusions sidebar button near the bottom. Checkboxes for all Clients are on by default.
To use this feature,
 or
or 
Now, the next time you do a normal export, the excluded items will be removed from the browsers whose checkboxes you switched off, and will not re-exported until you switch them back on.
Note that Export Exclusions are attributes of the bookmark or folder and are not Local Settings. That is, if your Collection is synced to or copied to other Macs, the same exclusions will apply to the same Clients (and all of their profiles).
When deleting all duplicates or consolidating folders, Smarky, Synkmark, Markster or BookMacster must decide for you which item to keep and which item to delete. As explained, in those sections, it retains the item with higher quality. Generally, items are compared two at a time to determine which has higher quality.
| Home | Parent | ← Go → | Prior | Next |